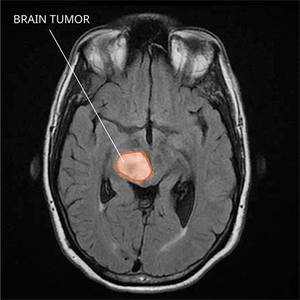
Brain Tumor
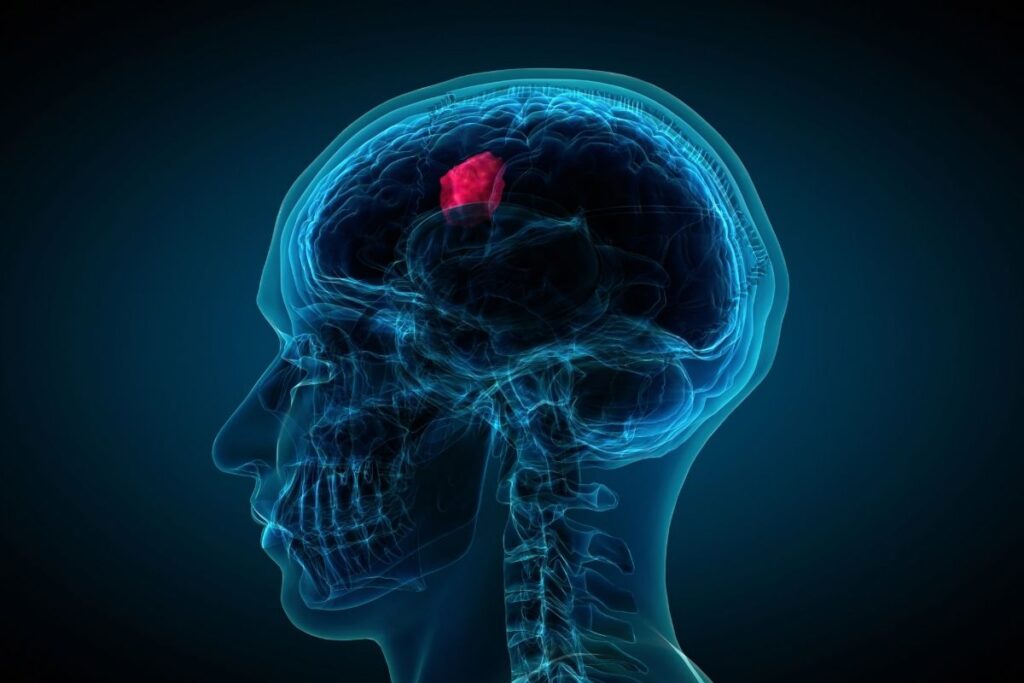
Brain Tumor
Brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in your brain.
Many different types of brain tumors exist. Some brain tumors are noncancerous (benign), and some brain tumors are cancerous (malignant). Brain tumors can begin in your brain (primary brain tumors), or cancer can begin in other parts of your body and spread to your brain as secondary (metastatic) brain tumors
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a brain tumor vary greatly and depend on the brain tumor’s size, location and rate of growth.
General signs and symptoms caused by brain tumors may include:
- New onset or change in pattern of headaches
- Headaches that gradually become more frequent and more severe
- Unexplained nausea or vomiting
- Vision problems, such as blurred vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision
- Gradual loss of sensation or movement in an arm or a leg
- Difficulty with balance
Treatment
Surgery is the usual treatment for most brain tumors. To remove a brain tumor, a neurosurgeon makes an opening in the skull. This operation is called a craniotomy. Whenever possible, the surgeon attempts to remove the entire tumor. If the tumor cannot be completely removed without damaging vital brain tissue, your doctor may remove as much of the tumor as possible. Partial removal helps to relieve symptoms by reducing pressure on the brain and reduces the amount of tumor to be treated by radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy, also called radiotherapy, is the use of high-powered rays to damage cancer cells and stop them from growing. It is often used to destroy tumor tissue that cannot be removed with surgery or to kill cancer cells that may remain after surgery. Radiation therapy also is used when surgery is not possible.
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The doctor may use just one drug or a combination, usually giving the drugs orally or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle. Intrathecal chemotherapy involves injecting the drugs into the cerebrospinal fluid.